Content Marketing
Drive Business Results with Google
Posted on .Topics
- Introduction to Online Advertising
- How to Reach Customers with Google Ads
- Reaching Customers with Local Services By Google – This is a Google Products service designed to assist local service providers and consumers.
- FAQs
Introduction to Online Advertising
A recent study by IFLSCIENCE shows that the average consumer spends approximately 6 hours and 42 minutes on the internet each day. For any business, this is great news. The internet is making best platform where potential customers can see you, particularly when they’re searching for information about the products and services that you offer.
For close to 20 years now, both small and large businesses have been using Google ads to appear on search result pages. These include web pages, videos, mobile apps, and so on.
Why Google Ads?
To start Advertising on Google, you can visit ads.google.com and you’ll create an account at no cost – no start up, cancellation, contract or minimum commitment fee requirement.
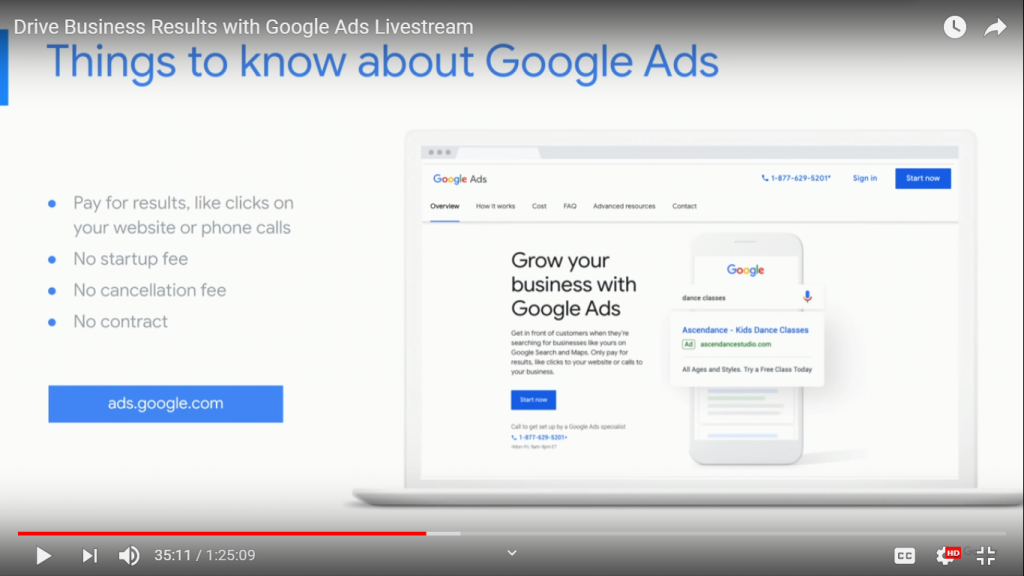
- You can easily track and measure performance – Online advertising does not need any pool of a sales pitch as the proof is in the results.
- Ease of budget control – You determine how much you want to spend on an advertising campaign and set it up easily.
- You can edit, pause or cancel your campaigns any time.
How Google Advertising Works
The search Process can be summarized in three steps.
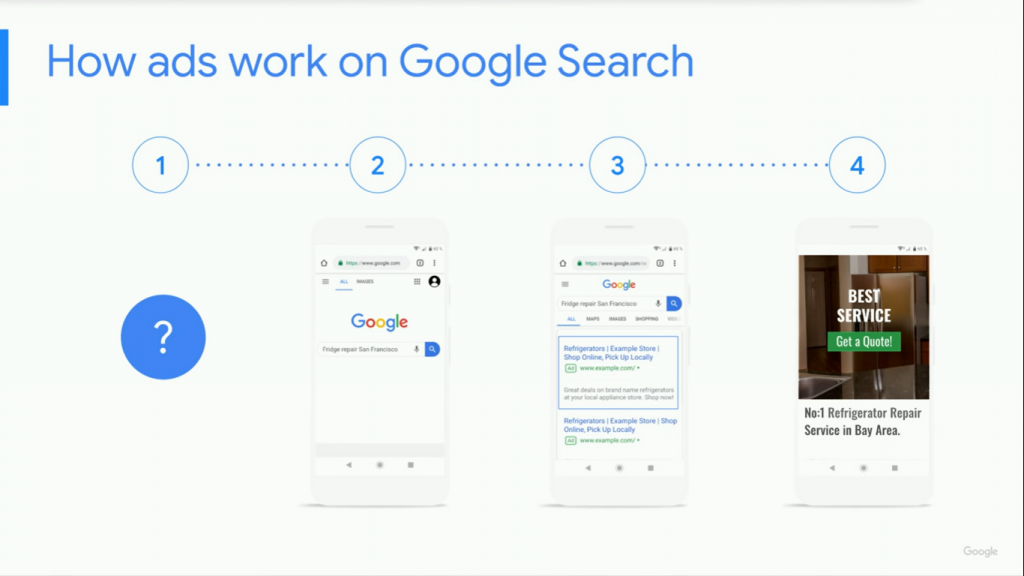
1. The Search Query
Advertisers use a Google product called Google Ads to run campaigns. The whole process begins with a question, desire, or a need. Most customers start their search process by typing a query into Google. From this, Google’s organic algorithm creates a Search Engine Result’s page (SERP) that presents websites and other resources that are relevant to the search query.
2. Auction
At the same time but separately, the Google algorithms run an auction. Auctions give advertisers a bidding chance for opportunities to show their ads. Eligible ads compete for a spot on the results page, both above and below organic results. Winners appear top on the page, clearly labeled with an Ads sticker.
3. Action
When searchers see the Ad, they take action by clicking on the search result that seems to suit or match their search query most. They could, for instance, make an action of visiting the website, placing a call on a mobile device, or calling a trackable number. These actions connect potential customers to advertisers and drive business results.
This is how ads may appear on Google’s search results page.
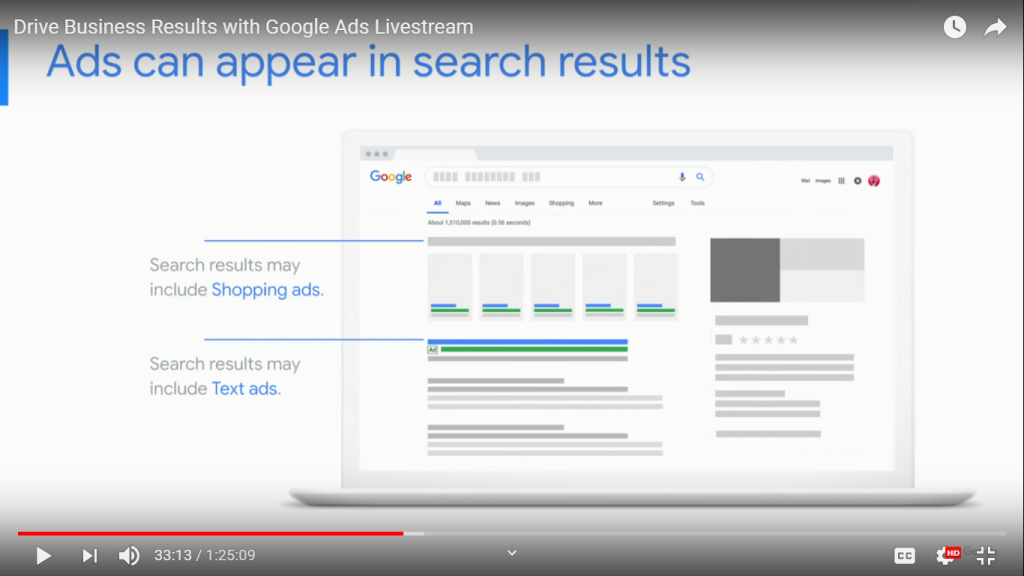
- Shopping ads appear at the very top as images with related product information.
- Text ads may be placed either on top of organic ads or below them. Advertisers don’t pay when the ads appear on the search engine results page. They are only charged once the searcher takes action by clicking that ad.
Ad Rank
Your Ad’s position on Google’s Results Page relative to that of other ads on the same page is determined by something called Ad Rank. Ad rank is calculated using:
- The Bid Amounts
- The Ad Quality at Auction Time:
Ad quality is measured by:
- Expected click-through rate (CTR)
- Relevance
- Landing page experience
- Ad rank threshold
- The search context
The context of an ad may be affected by the searcher’s location, the device he/she is using, the expected impact of ad extensions and the time of the search among other signals.
Ad rank is recalculated every single time a search is made, and every eligible Ad competes in the auction. This means that the position may fluctuate depending on the competition, the person’s search, and the quality at the moment of the search.
Google Display Network
Ads may also appear on other Google sites like Gmail, YouTube and over 2 Million non-google websites that are part of the Google Display Network (GDN). The Google Display network reaches 90% of internet users across the globe and can show in many formats including videos, images, and text ads.
Bidding Options in the Display Network
- Pay Per Click (PPC) – PPC is also known as Cost Per Click (CPC). This requires advertisers to pay for a click on the result’s page or any desired action
- Cost Per Mile (CPM) – Advertisers who use CPM pay per one thousand impressions/ visitors who see their advertisements.
- Cost Per View (CPV) – Applies to video ads.
How to Set a Campaign that Drives Business Results
- Clarify your goals – goals may include sales, leads, or web traffic
- Decide where you want your ads to appear
- Describe the product or service you are advertising
- Write your ad
- Set a budget
- Launch your campaign
Setting Goals on Google Campaigns
Goal 1: Driving Sales
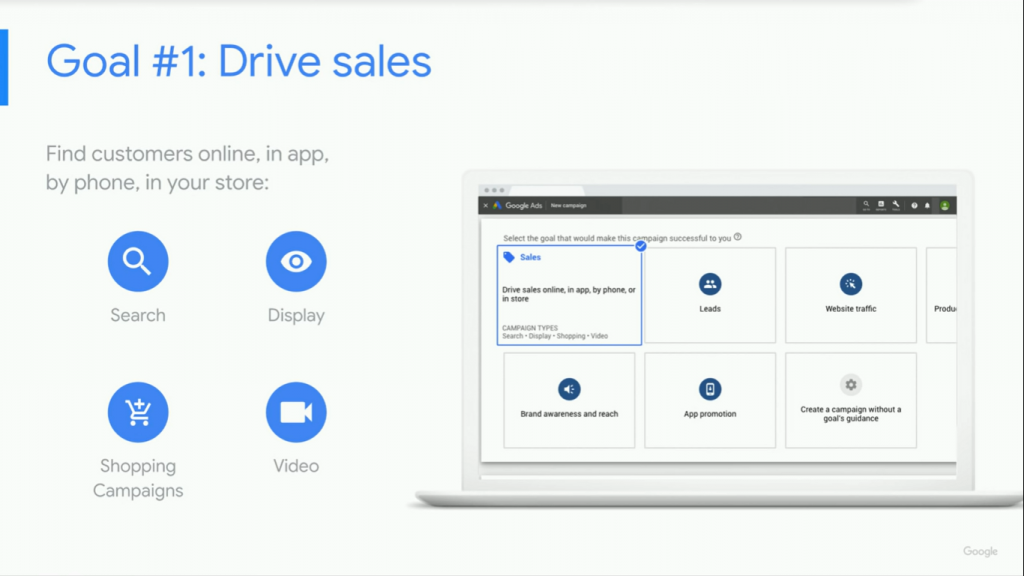
When you first create a campaign in Google ads, you’ll see an option to create a goal. You can choose any of the following goals for your advertising campaign:
- Driving sales
- Generating Leads
- Creating Website Traffic
- Enhancing Brand Awareness and Reach
- App promotion.
Google recommends the use of Search, Display, shopping and video campaigns to reach a sale’s driving goal. It is also advisable that you set up features that enable you to track and measure campaign success. You can achieve this through:
- Conversion tracking
- Google analytics
Smart Campaigns
Google’s smart campaigns are designs for small businesses that want to promote their products or services online. Smart campaigns allow you to set up goals like:
- Calls
- More store visits
- Actions on your website
- And more!
- A Smart campaign is easy to set up and use smart technology to monitor and improve your Ad’s performance continuously. One benefit of using smart campaigns is that the process of setting up an ad is automated. Here’s how a Smart campaign will be beneficial:
- An easier time managing the campaign – most work is done for you.
- You don’t need to develop keyword lists for a smart campaign. The system automatically generates a search phrase based on the nature of your ad.
- You can disable search queries that don’t match your campaign for better interaction.
- Setting up a Smart Campaign
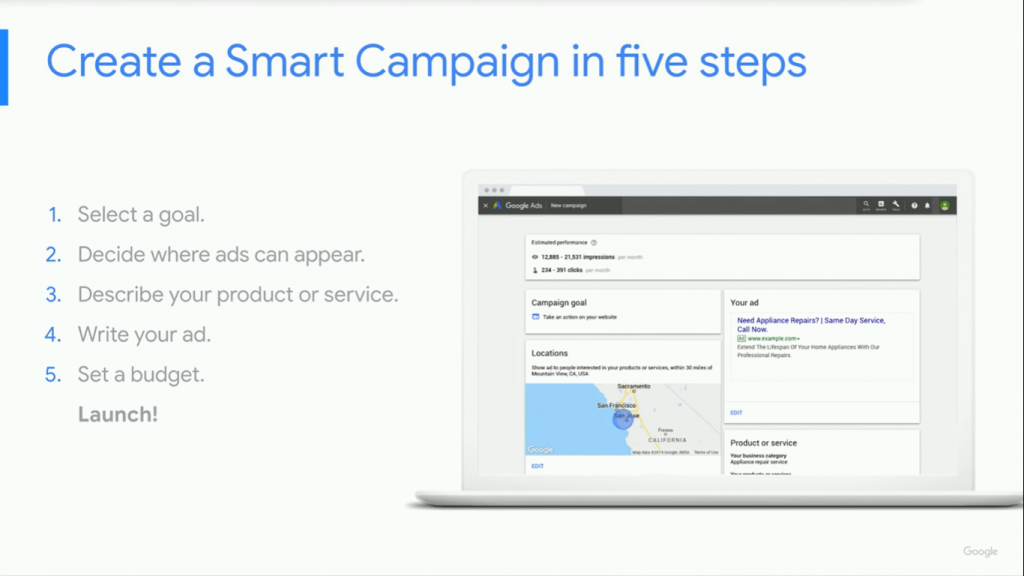
- Come up with a goal
- Decide where you want your ads to appear – geologically
- Describe the product or service you are selling
- Write your ad
- Set up a budget
- Launch your campaign
Goal 2: Generating Leads
If you don’t sell products or services directly via your website, a sales goal may not work for you. This especially applies to handymen or repair technicians like plumbers, electricians, builders, and landscapers among others. For such businesses, the campaign could be lead generation, a request for a quote, or a scheduled appointment.
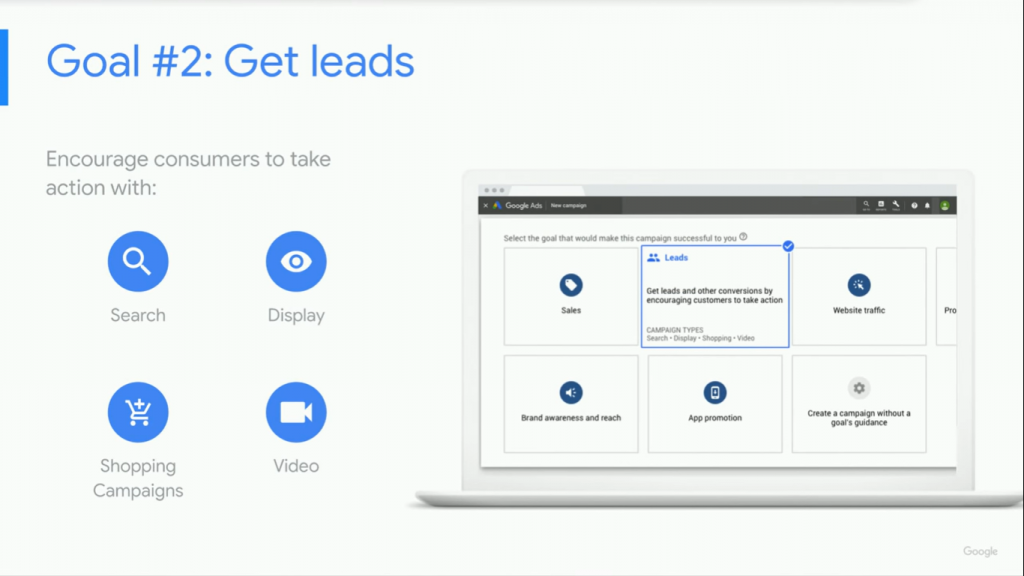
On lead generation, Google encourages the use of Search, Display, Shopping, and Video campaigns.
Search Campaigns
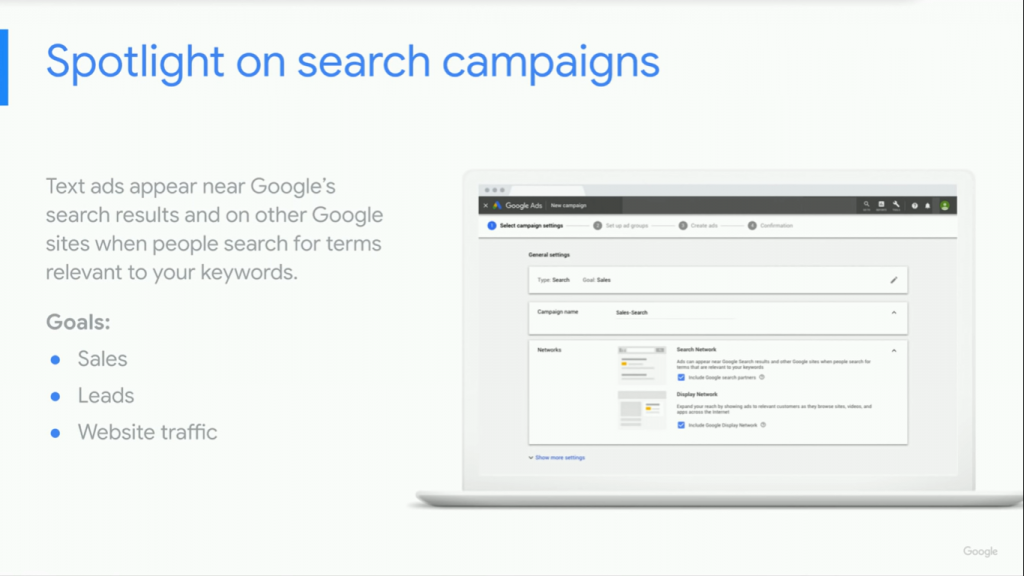
When someone searches something on Google, search ads appear either below or above organic search results. These ads are usually shown for relevant searches. On search ads, you can set goals such as sales, leads, and web traffic.
A search text ad has three parts
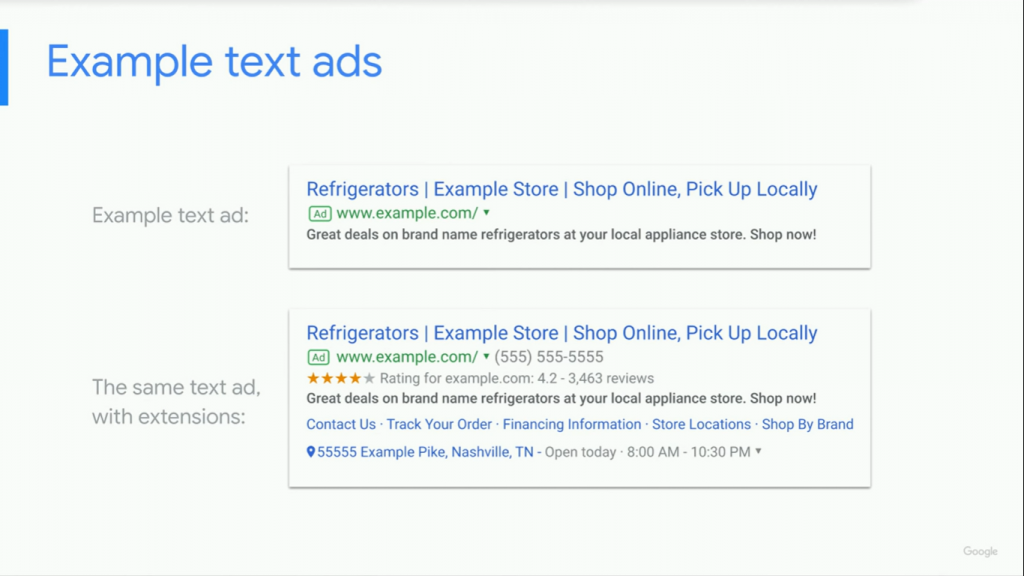
A Headline – You can promote your product or service in three separate headlines. These are separated by a vertical pipe symbol and may appear differently depending on the searcher’s device
A Display URL – This shows your web address. It is made up of the domain from your final URL and optional texts you can enter on your path fields. The path text gives people an idea of where they will be going after clicking on your ad. The path text does not have to match the exact language of your display URL.
The Description – This highlights details about the product you are advertising. You may describe features, benefits, promotions, discounts, shipping options and more. You can enhance your advertising results by including a Call To Action here encouraging potential customers to take the next step.
Character limits for a Search text:
- Headline 1 – 30 Characters
- Headline 2 – 30 Characters
- Headline 3 – 30 Characters
- 1st description line – 90 characters
- 2nd description line – 90 characters
- Optional fields added to the final URL – 15 characters each.
- Extensions
- Extensions expand ads with more information. These extra information snippets increase the click-through rate (the ratio of people who see an ad vs who click it) and on ways through which people can reach you. Extensions may be added in the form of:
- Call Buttons
- Text buttons
- Location Information
- Links to specific areas of a website
- Application download
- Additional text
- And more!
Google ads select which extensions to show in response to every Google search. For this reason, it is advisable that you use all extensions that are in line with your business goals. However, adding extensions does not guarantee that it will show with the ad. They only show up when Google feels that they will improve performance and when your ad position and rank meet the set threshold.
There are two types of extensions: Automatic and Manual. Automatic extensions are added automatically by when Google ads predict that they will enhance ad performance. You’ll need some set up the latter manually.
Adding extensions is free but if people clicks on them, you will be charged as usual. The only exemption to this is if a click is on a seller rating as this will not cost you.
Note: Google does not charge more than two clicks per impression for each ad and its extensions.
Comments are closed.